Challenge: dynamic_1
Bypass complex hashing logic to find the valid key using GDB.
Step 1: Initial Static Assessment
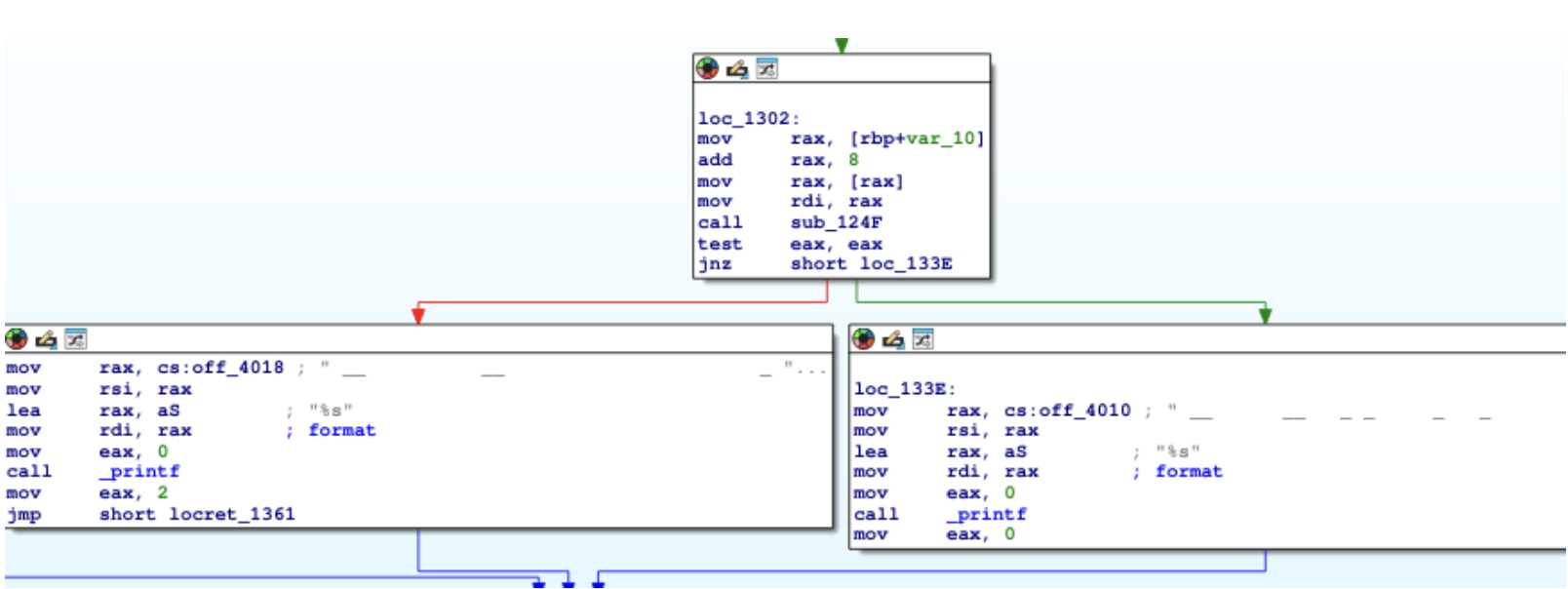
We started by observing the verification flow in IDA Pro. The program
ensures an argument is provided (argc > 1) and
passes it to sub_124F for the main validation logic.
Step 2: Identifying the Target
Inside sub_124F, we found that the program loads a decoy string ("This is not the password") and calls
sub_11A9 to calculate a hash.
The static logic revealed that this hash is converted to a hex string via
sprintf and stored in a buffer. This buffer is then compared against our
user input. This is our vulnerability: catching the hash in memory before the
comparison.
Step 3: GDB Breakpoint Strategy
Instead of manually calculating the DJB2-modified hash, we used
GDB to catch the password in memory. Since the binary has no symbols,
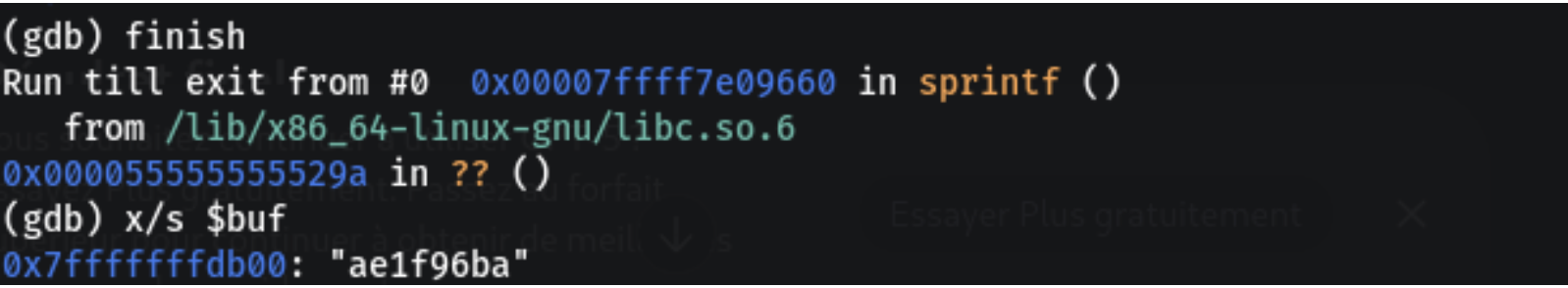
we placed a breakpoint on the sprintf library call.
Step 4: Memory Observation
When we hit the breakpoint, the rdi register
contained the address of our destination buffer.
We saved the buffer address and let the function finish executing to see the generated string in memory.
Step 5: Final Validation
The generated hash ae1f96ba is the exact value
required to pass the check.