Challenge: Static_1
Documenting the initial approach to binary analysis through the Static_1 challenge. This walkthrough outlines the methodology for identifying key validation logic and extracting credentials from binary data.
Step 1: Initial Execution (The Reality Check)
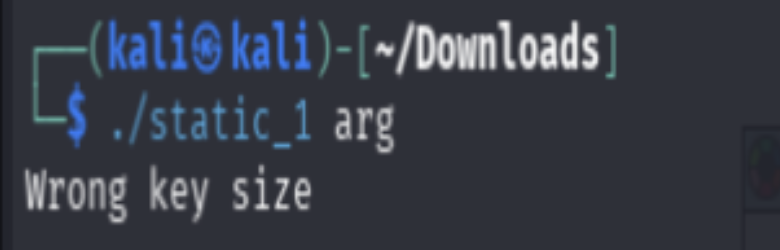
Initial execution of the binary ./static_1 arg yields an error message
indicating a validation failure:
Wrong key size
Step 2: Identifying Key Length
The next obvious step was looking for the right key length using IDA Pro. No point in guessing when you can just read the instructions written in assembly.
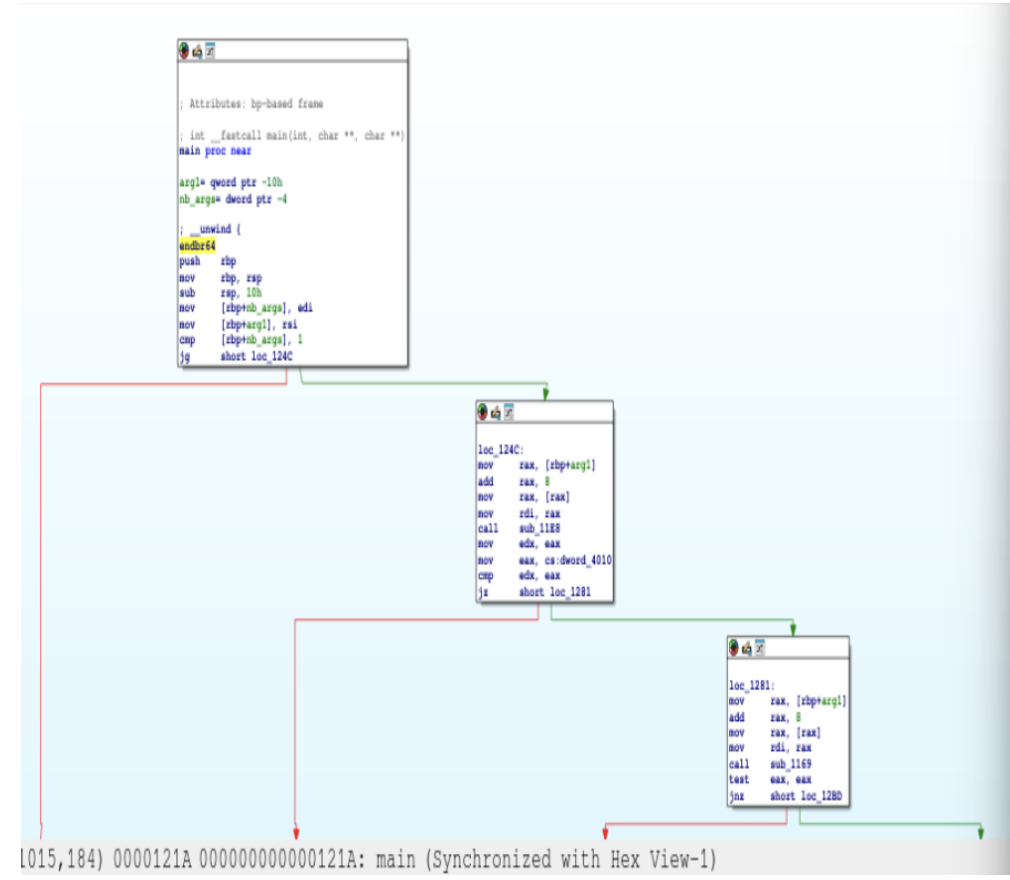
We followed the logic tree and identified argc and argv. We
found that dword_4010 held the gatekeeper value for our input:
0Bh.
Conversion: 0Bh in Hex = 11 in Decimal.

Step 3: Tracing the Validation Logic
With the key length established, we proceeded to analyze the core validation logic by
tracing the sub_1169 function call.
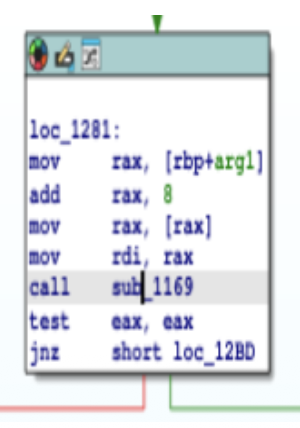
Decompilation of sub_1169 reveals an XOR-based validation loop, which
serves as the primary mechanism for input verification.
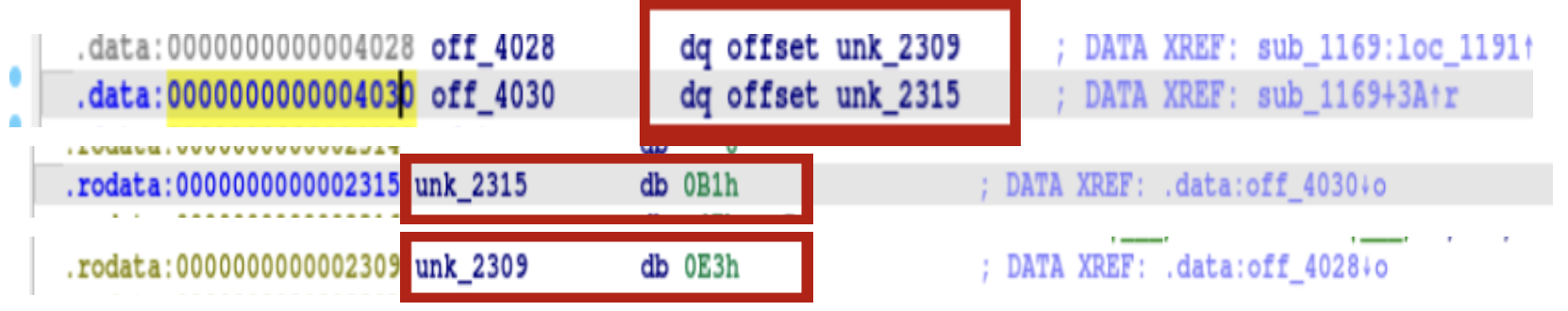
Logic Breakdown:
off_4028 (String A).
off_4030 (String B/Key component).
xor ecx, eax: It XORs these bytes together, repeating until the
end of the strings.
Step 4: Final Calculation
The flag is reconstructed by extracting the data from the identified memory addresses and performing the XOR operation on the source strings.
unk_2309 (Source A): E3 2E FF 2F 56 47 C2 33 F0 21 OF
unk_2315 (Source B): B1 47 9C 44 76 06 B1 47 9C 44 76
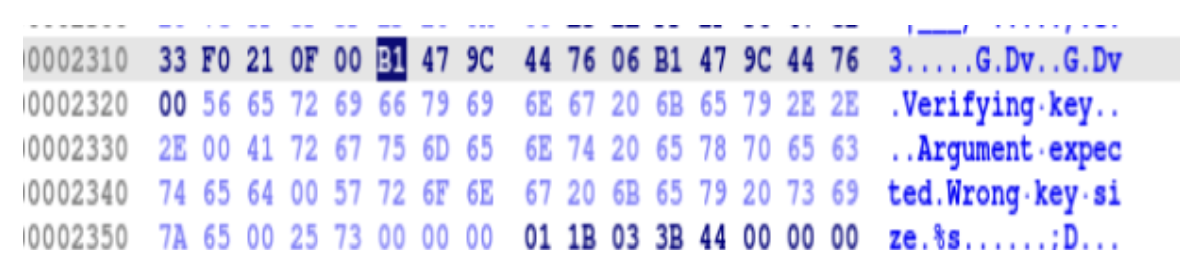
Final Result: Input Verification
XORing these two 11-byte strings reveals the ultimate answer:
Upon executing the binary with the derived key, the system confirms visibility of the correct flag, completing the analysis.
